H Cation Lewis Structure
Representing Valence Electrons in Lewis Symbols
Zundel cation A hydrogen atom is made up of a nucleus with charge +1, and a single electron. Therefore, the only positively charged ion possible has charge +1. It is noted H +. When the Lewis structure of an ion is written, the entire structure is placed in brackets, and the charge is written as a superscript on the upper right, outside of the brackets. For example, consider the ammonium ion, NH 4 +, which contains 9 (5 from N and 1 from each of the four H atoms) –1 = 8 electrons.
Rules for Writing Lewis Structures. Count the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or polyatomic ion. (For example, H 2 O has 2x1 + 6 = 8 valence electrons, CCl 4 has 4 + 4x7 = 32 valence electrons.) For anions, add one valence electron for each unit of negative charge; for cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge. The Lewis symbol, more commonly 'Lewis structure,' of H+ is just H The hydrogen has been stripped of its only electron to form the positive ion.
Lewis symbols use dots to visually represent the valence electrons of an atom.
Learning Objectives
Recall the Lewis structure formalism for representing valance electrons
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Electrons exist outside of an atom ‘s nucleus and are found in principal energy levels that contain only up to a specific number of electrons.
- The outermost principal energy level that contains electrons is called the valence level and contains valence electrons.
- Lewis symbols are diagrams that show the number of valence electrons of a particular element with dots that represent lone pairs.
- Lewis symbols do not visualize the electrons in the inner principal energy levels.
Key Terms
- principal energy levels: The different levels where electrons can be found and that occur at specific distances from the atom’s nucleus. Each level is associated with a particular energy value that electrons within it have.
- valence level: The outermost principal energy level, which is the level furthest away from the nucleus that still contains electrons.
- valence electrons: The electrons of atoms that participate in the formation of chemical bonds.
- Lewis symbols: Symbols of the elements with their number of valence electrons represented as dots
Lewis symbols (also known as Lewis dot diagrams or electron dot diagrams) are diagrams that represent the valence electrons of an atom. Lewis structures (also known as Lewis dot structures or electron dot structures) are diagrams that represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. These Lewis symbols and Lewis structures help visualize the valence electrons of atoms and molecules, whether they exist as lone pairs or within bonds.
Principal Energy Levels
An atom consists of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons. The electrostatic attraction between them keeps electrons ‘bound’ to the nucleus so they stay within a certain distance of it. Careful investigations have shown that not all electrons within an atom have the same average position or energy. We say the electrons ‘reside’ in different principal energy levels, and these levels exist at different radii from the nucleus and have rules regarding how many electrons they can accommodate.
Principal energy levels of gold (Au): The figure shows the organization of the electrons around the nucleus of a gold (Au) atom. Notice that the first energy level (closest to the nucleus) can have only two electrons, while more electrons can ‘fit’ within a given level further out. The number of electrons in each level is listed on the upper right corner of the figure. Notice that the outermost level has only one electron.
As an example, a neutral atom of gold (Au) contains 79 protons in its nucleus and 79 electrons. The first principal energy level, which is the one closest to the nucleus, can hold a maximum of two electrons. The second principal energy level can have 8, the third can have 18, and so on, until all 79 electrons have been distributed.
The outermost principal energy level is of great interest in chemistry because the electrons it holds are the furthest away from the nucleus, and therefore are the ones most loosely held by its attractive force; the larger the distance between two charged objects, the smaller the force they exert on each other. Chemical reactivity of all of the different elements in the periodic table depends on the number of electrons in that last, outermost level, called the valence level or valence shell. In the case of gold, there is only one valence electron in its valence level.
Octet of Valence Electrons
Atoms gain, lose, or share electrons in their valence level in order to achieve greater stability, or a lower energy state. From this perspective, bonds between atoms form so that the bonded atoms are in a lower energy state compared to when they were by themselves. Atoms can achieve this more stable state by having a valence level which contains as many electrons as it can hold. For the first principal energy level, having two electrons in it is the most stable arrangement, while for all other levels outside of the first, eight electrons are necessary to achieve the most stable state.
Lewis Symbols
In the Lewis symbol for an atom, the chemical symbol of the element (as found on the periodic table) is written, and the valence electrons are represented as dots surrounding it. Only the electrons in the valence level are shown using this notation. For example, the Lewis symbol of carbon depicts a “C’ surrounded by 4 valence electrons because carbon has an electron configuration of 1s22s22p2.
The Lewis symbol for carbon: Each of the four valence electrons is represented as a dot.
Electrons that are not in the valence level are not shown in the Lewis symbol. The reason for this is that the chemical reactivity of an atom of the element is solely determined by the number of its valence electrons, and not its inner electrons. Lewis symbols for atoms are combined to write Lewis structures for compounds or molecules with bonds between atoms.
Writing Lewis Symbols for Atoms
The Lewis symbol for an atom depicts its valence electrons as dots around the symbol for the element.
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- The columns, or groups, in the periodic table are used to determine the number of valence electrons for each element.
- The noble/ inert gases are chemically stable and have a full valence level of electrons.
- Other elements react in order to achieve the same stability as the noble gases.
- Lewis symbols represent the valence electrons as dots surrounding the elemental symbol for the atom.
Key Terms
- group: A column in the periodic table that consists of elements with similar chemical reactivity, because they have the same number of valence electrons.
- Noble Gases: Inert, or unreactive, elements in the last group in the periodic table which are typically found in the gaseous form.
- Lewis symbol: Formalism in which the valence electrons of an atom are represented as dots.
Determining the Number of Valence Electrons
In order to write the Lewis symbol for an atom, you must first determine the number of valence electrons for that element. The arrangement of the periodic table can help you figure out this information. Since we have established that the number of valence electrons determines the chemical reactivity of an element, the table orders the elements by number of valence electrons.
Each column (or group) of the periodic table contains elements that have the same number of valence electrons. Furthermore, the number of columns (or groups) from the left edge of the table tells us the exact number of valence electrons for that element. Recall that any valence level can have up to eight electrons, except for the first principal energy level, which can only have two.
Periodic table of the elements: Group numbers shown by Roman numerals (above the table) tell us how many valence electrons there are for each element.
Some periodic tables list the group numbers in Arabic numbers instead of Roman numerals. In that case, the transition metal groups are included in the counting and the groups indicated at the top of the periodic table have numbers 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18. The corresponding roman numerals used are I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII.
Survey of the Groups in the Periodic Table
Take the first column or group of the periodic table (labeled ‘I’): hydrogen (H), lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), etc. Each of these elements has one valence electron. The second column or group (labeled ‘II’) means that beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), etc., all have two valence electrons.
The middle part of the periodic table that contains the transition metals is skipped in this process for reasons having to do with the electronic configuration of these elements.
Proceeding to the column labeled ‘III’, we find that those elements (B, Al, Ga, In,…) have three valence electrons in their outermost or valence level.
We can continue this inspection of the groups until we reach the eighth and final column, in which the most stable elements are listed. These are all gaseous under normal conditions of temperature and pressure, and are called ‘noble gases.’ Neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), etc., each contain eight electrons in their valence level. Therefore, these elements have a full valence level that has the maximum number of electrons possible. Helium (He), at the very top of this column is an exception because it has two valence electrons; its valence level is the first principal energy level which can only have two electrons, so it has the maximum number of electrons in its valence level as well.
The Lewis symbol for helium: Helium is one of the noble gases and contains a full valence shell. Unlike the other noble gases in Group 8, Helium only contains two valence electrons. In the Lewis symbol, the electrons are depicted as two lone pair dots.
The noble gases represent elements of such stability that they are not chemically reactive, so they can be called inert. In other words, they don’t need to bond with any other elements in order to attain a lower energy configuration. We explain this phenomenon by attributing their stability to having a ‘full’ valence level.
The significance in understanding the nature of the stability of noble gases is that it guides us in predicting how other elements will react in order to achieve the same electronic configuration as the noble gases by having a full valence level.
Writing Lewis Symbols for Atoms
Lewis symbols for the elements depict the number of valence electrons as dots. In accordance with what we discussed above, here are the Lewis symbols for the first twenty elements in the periodic table. The heavier elements will follow the same trends depending on their group.
Once you can draw a Lewis symbol for an atom, you can use the knowledge of Lewis symbols to create Lewis structures for molecules.
Valence Electrons and the Periodic Table: Electrons can inhabit a number of energy shells. Different shells are different distances from the nucleus. The electrons in the outermost electron shell are called valence electrons, and are responsible for many of the chemical properties of an atom. This video will look at how to find the number of valence electrons in an atom depending on its column in the periodic table.
Introduction to Lewis Structures for Covalent Molecules
In covalent molecules, atoms share pairs of electrons in order to achieve a full valence level.
Learning Objectives
Predict and draw the Lewis structure of simple covalent molecules and compounds
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- The octet rule says that the noble gas electronic configuration is a particularly favorable one that can be achieved through formation of electron pair bonds between atoms.
- In many atoms, not all of the electron pairs comprising the octet are shared between atoms. These unshared, non-bonding electrons are called ‘ lone pairs ‘ of electrons.
- Although lone pairs are not directly involved in bond formation, they should always be shown in Lewis structures.
- There is a logical procedure that can be followed to draw the Lewis structure of a molecule or compound.
Key Terms
- octet rule: Atoms try to achieve the electronic configuration of the noble gas nearest to them in the periodic table by achieving a full valence level with eight electrons.
- exceptions to the octet rule: Hydrogen (H) and helium (He) only need two electrons to have a full valence level.
- covalent bond: Two atoms share valence electrons in order to achieve a noble gas electronic configuration.
- Lewis structure: Formalism used to show the structure of a molecule or compound, in which shared electrons pairs between atoms are indicated by dashes. Non-bonding, lone pairs of electrons must also be shown.
The Octet Rule
Noble gases like He, Ne, Ar, Kr, etc., are stable because their valence level is filled with as many electrons as possible. Eight electrons fill the valence level for all noble gases, except helium, which has two electrons in its full valence level. Other elements in the periodic table react to form bonds in which valence electrons are exchanged or shared in order to achieve a valence level which is filled, just like in the noble gases. We refer to this chemical tendency of atoms as ‘the octet rule,’ and it guides us in predicting how atoms combine to form molecules and compounds.
Covalent Bonds and Lewis Diagrams of Simple Molecules
The simplest example to consider is hydrogen (H), which is the smallest element in the periodic table with one proton and one electron. Hydrogen can become stable if it achieves a full valence level like the noble gas that is closest to it in the periodic table, helium (He). These are exceptions to the octet rule because they only require 2 electrons to have a full valence level.
Two H atoms can come together and share each of their electrons to create a ‘ covalent bond.’ The shared pair of electrons can be thought of as belonging to either atom, and thus each atom now has two electrons in its valence level, like He. The molecule that results is H2, and it is the most abundant molecule in the universe.
Lewis structure of diatomic hydrogen: This is the process through which the H2 molecule is formed. Two H atoms, each contributing an electron, share a pair of electrons. This is known as a ‘single covalent bond.’ Notice how the two electrons can be found in a region of space between the two atomic nuclei.
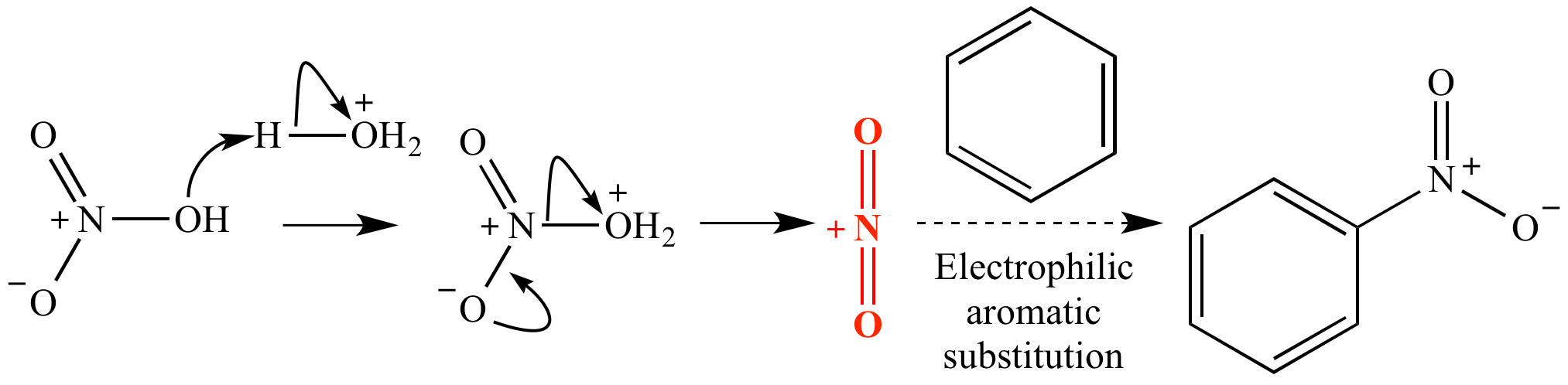
H Cation Lewis Structure
The Lewis formalism used for the H2 molecule is H:H or H—H. The former, known as a ‘Lewis dot diagram,’ indicates a pair of shared electrons between the atomic symbols, while the latter, known as a ‘Lewis structure,’ uses a dash to indicate the pair of shared electrons that form a covalent bond. More complicated molecules are depicted this way as well.
Lewis dot dragram for methane: Methane, with molecular formula CH4, is shown. The electrons are color-coded to indicate which atoms they belonged to before the covalent bonds formed, with red representing hydrogen and blue representing carbon. Four covalent bonds are formed so that C has an octet of valence electrons, and each H has two valence electrons—one from the carbon atom and one from one of the hydrogen atoms.
Now consider the case of fluorine (F), which is found in group VII (or 17) of the periodic table. It therefore has 7 valence electrons and only needs 1 more in order to have an octet. One way that this can happen is if two F atoms make a bond, in which each atom provides one electron that can be shared between the two atoms. The resulting molecule that is formed is F2, and its Lewis structure is F—F.
Achieving an octet of valence electrons: Two fluorine atoms are able to share an electron pair, which becomes a covalent bond. Notice that only the outer (valence level) electrons are involved, and that in each F atom, 6 valence electrons do not participate in bonding. These are ‘lone pairs’ of electrons.
After a bond has formed, each F atom has 6 electrons in its valence level which are not used to form a bond. These non-bonding valence electrons are called ‘lone pairs’ of electrons and should always be indicated in Lewis diagrams.
Lewis structure of acetic acid: Acetic acid, CH3COOH, can be written out with dots indicating the shared electrons, or, preferably, with dashes representing covalent bonds. Notice the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atoms are still shown. The methyl group carbon atom has six valence electrons from its bonds to the hydrogen atoms because carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen. Also, one electron is gained from its bond with the other carbon atom because the electron pair in the C−C bond is split equally.
Procedure for Drawing Simple Lewis Structures
We have looked at how to determine Lewis structures for simple molecules. The procedure is as follows:
- Write a structural diagram of the molecule to clearly show which atom is connected to which (although many possibilities exist, we usually pick the element with the most number of possible bonds to be the central atom).
- Draw Lewis symbols of the individual atoms in the molecule.
- Bring the atoms together in a way that places eight electrons around each atom (or two electrons for H, hydrogen) wherever possible.
- Each pair of shared electrons is a covalent bond which can be represented by a dash.
Alternate view of lewis dot structure of water: This arrangement of shared electrons between O and H results in the oxygen atom having an octet of electrons, and each H atom having two valence electrons.
Multiple bonds can also form between elements when two or three pairs of electrons are shared to produce double or triple bonds, respectively. The Lewis structure for carbon dioxide, CO2, is a good example of this.
Lewis structure of carbon dioxide: This figure explains the bonding in a CO2 molecule. Each O atom starts out with six (red) electrons and C with four (black) electrons, and each bond behind an O atom and the C atom consists of two electrons from the O and two of the four electrons from the C.
In order to achieve an octet for all three atoms in CO2, two pairs of electrons must be shared between the carbon and each oxygen. Since four electrons are involved in each bond, a double covalent bond is formed. You can see that this is how the octet rule is satisfied for all atoms in this case. When a double bond is formed, you still need to show all electrons, so double dashes between the atoms show that four electrons are shared.
Final Lewis structure for carbon dioxide: Covalent bonds are indicated as dashes and lone pairs of electrons are shown as pairs of dots. in carbon dioxide, each oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons remaining; the covalent bonds between the oxygen and carbon atoms each use two electrons from the oxygen atom and two from the carbon.
Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions
The Lewis structure of an ion is placed in brackets and its charge is written as a superscript outside of the brackets, on the upper right.
Learning Objectives
Apply the rules for drawing Lewis structures to polyatomic ions
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Ions are treated almost the same way as a molecule with no charge. However, the number of electrons must be adjusted to account for the net electric charge of the ion.
- When counting electrons, negative ions should have extra electrons placed in their Lewis structures, while positive ions should have fewer electrons than an uncharged molecule.
Key Terms
- polyatomic ion: A charged species composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded, or of a metal complex that acts as a single unit in acid-base chemistry or in the formation of salts. Also known as a molecular ion.
The total number of electrons represented in a Lewis structure is equal to the sum of the numbers of valence electrons in each individual atom. Non-valence electrons are not represented in Lewis structures. After the total number of available electrons has been determined, electrons must be placed into the structure.
Lewis structures for polyatomic ions are drawn by the same methods that we have already learned. When counting electrons, negative ions should have extra electrons placed in their Lewis structures; positive ions should have fewer electrons than an uncharged molecule. When the Lewis structure of an ion is written, the entire structure is placed in brackets, and the charge is written as a superscript on the upper right, outside of the brackets. For example, consider the ammonium ion, NH4+, which contains 9 (5 from N and 1 from each of the four H atoms) –1 = 8 electrons. One electron is subtracted because the entire molecule has a +1 charge.
Coordinate covalent bonding: The ammonium ion, NH4+, contains 9–1 = 8 electrons.
Negative ions follow the same procedure. The chlorite ion, ClO2–, contains 19 (7 from the Cl and 6 from each of the two O atoms) +1 = 20 electrons. One electron is added because the entire molecule has a -1 charge.
Hypochlorite ion Lewis structure: The hypochlorite ion, ClO−, contains 13 + 1 = 14 electrons.
Lewis dot structure is the classical bonding model in which only valence electrons of the atoms are used. Lewis structure is very important in chemistry, because they are used in many important concepts of general chemistry such as chemical bonding, resonance, valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, prediction of the polarity of the molecules and understanding of reaction mechanisms. Hence it is very important to learn how to draw Lewis Dot structure correctly for an atom, ion, molecule, polyatomic ion and an ionic compound.
We can learn to make accurate Lewis dot structures in 4 simple steps. These steps are easy to understand and implement. Do not skip or try to rearrange any step during your learning process, as it is important to understand and implement each step to correctly design these structures. Once you master these, you can draw Lewis structure of any chemical entity quickly. In these steps, you will come across some terms like valence electrons ,electronegativity, stable electronic configuration, formal charges, bonding pair and lone pair, single ,double and triple bonds .If you do not know the meaning of any of these terms, do not worry as all terms will be explained in the explanation of each step .
STEP 1 : COUNT THE TOTAL VALENCE ELECTRONS.
In Lewis dot structure, only valence electrons are used for making of the structure. Valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost shell of the electronic configuration of an atom. The example below should shed some light on this.
Valence electrons of Nitrogen atom and Chlorine atom
If you are not good at writing electronic configurations, then there is another easy way of predicting the valence electrons by using the periodic table. Valence electrons are equal to the group number of the element in the periodic table. You can work some examples on the periodic table right now:
O belongs to group number 6 and its valence electrons are also 6.
Be belongs to group number 2 and its valence electrons are also 2.
Well, that’s step one! Easy, isn’t it?
Calculating valence electrons with the help of the periodic table
Lewis dot structure for an atom:
For neutral atoms only step one is required. Just use dots for valence electrons (outermost shell electrons) and place them as paired and unpaired around the four sides of the symbol of the atom as presented in the electronic configuration of the element. For example
Nitrogen atom:
Electronic configuration:
[He]2s22p3
Valence shell is 2s22p3 with total 5 electrons.
Let’s do one more example:
Se atom

Electronic configuration:
[Ar]3d104s24p4
Valence shell is 4s24p4 with total 6 electrons.
Lewis dot structure of Se atom
Lewis dot structure of all atoms of the main periodic table
Lewis dot structure of Monoatomic ions:
Ions are formed by gain or loss of electrons, so this will change the total number of valence electrons in the ion for the Lewis dot structure .If an atom has a negative charge it means it has gained electrons equal to the charge present on that ion, and in case of a positive charge, it has lost electrons .No of electrons lost or gained are subtracted or added from the valence electrons of the neutral atom.
For an example, let’s find the Lewis dot structure of a nitride ion ( N3-).Three negative charges means nitrogen atom has gained three electrons so its electronic configuration is with 10 electrons (instead of 7).
[He]2s22p6
Valence electrons are 8 (2 in 2s and 6 in 2p)
Now let us try Lewis dot structure of Sulfide ion ( S2-).Two negative charges means sulfur atom has gained two electrons so its electronic configuration is with 18 electrons (instead of 16).
[Ne]4s24p6
Valence electrons are 8 (2 in 3s and 6 in 3p)
Lewis dot structure of sulfide ion
Lewis dot structure will have 4 paired dots around Sulfur atom.For atoms and monoatomic ions, step one is sufficient to get the correct Lewis structure.
Lewis dot structures for Polyatomic ions and molecules :
However for molecules and polyatomic ions we need to consider many more factors before drawing a correct Lewis dot structure. Let’s practice step one “count the total valence electrons’ on molecules and polyatomic ions.
Molecule:
SO2 (Sulfur dioxide)
S is in the 6th group and O is also in the same group in the periodic table.
Total valence electrons = 6(S) + 2*6(2O) = 6+12=18
Ion:
NO3– (nitrate ion)
H Cation Lewis Structure Definition
Total valence electrons = 5(N) + 3*6(3O) +1 (-1 charge) = 5+18+1=24
STEP 2 : MAKE A SKELETON OF THE STRUCTURE
SELECT LEAST ELECTRO-NEGATIVE (EN) ATOM AS THE CENTRAL ATOM AND MAKE A SKELETON OF THE STRUCTURE WITH REST OF THE ATOMS AROUND IT
For selecting the central atom we should have a good knowledge of the electronegativity and electronegativity trends along the period and down the group.
Electronegativity (EN) is the tendency of an atom to pull a shared pair electrons which results in the polarity (charge separation) in the bond.
In a periodic table, EN decreases down the group (as the size of the atom increases) and increases along the period (as the size of the atom decreases). As the size of the atom increases bonded electrons move away from the nucleus of the atom and hence nucleus of atom will have less pull on the electrons.
EN and size of the atom
Here is a table that depicts electronegativity trends in the periodic table
Now let us select least EN atom as the central atom in our molecule SO2.You can use the periodic table while deciding about it. S is placed below O in the periodic table and hence it is bigger in size and less EN than O.
SO2 S is the central atom because S is less EN then O
In the skeleton of the molecule two oxygen atoms making single bonds with S
NO3– N is the central atom because N is less EN then O .In the skeleton of the ion three O atoms making three single bonds with central atom N.
Remember:
1. Central atom must be able to make more than 1 single bond around it.
2. First group elements (H and He) cannot have more than 2 electrons, since they have only 1s orbitals in their configurations.
Second period elements (C,N,O,F) cannot have more than 8 electrons around the central atom. This is due to the lack of empty d orbitals and hence these elements can not have expanded octet.
Elements from the third period onwards can have an expanded octet due to the introduction of d orbitals in these periods.
3. H and F can never be the central atom as they need only one electron to complete their respective duplet and octet. These elements make only single bonds with other elements.
STEP 3 : COMPLETE THE OCTET.
COMPLETE THE OCTET OF THE MOST ELECTRONEGATIVE ATOM WITH MINIMUM FORMAL CHARGES
Formal charge is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule or ion on the basis of the difference in valence electrons and electrons used by the atom in the Lewis dot structure. It is defined as the valence electrons of the atom minus electrons used by atom in making bonds and as lone pairs. An atom is supposed to use all electrons of its valence shell, but if it uses more or less than the number of electrons in its valence shell, then it gets a formal charge. For every covalent bond, an atom gives one electron so number of bonds around each atom will give the number of electrons used in making covalent bonds. Similarly for every lone pair it uses a pair of electrons.
Hence formal charge = valence electrons – electrons used (for bonding and as lone pair) in the Lewis dot structure

Formal charge (FC) = Valence electrons – ½ electrons as bond pairs – electrons as lone pairs
As we know, valence electrons are equal to the group number, number of bonds is equal to the number of electrons used in making covalent bonds and each lone pair means two electrons. So, the equation can be re-written as:
FC = Group No – No of bonds – 2*No of lone pairs.
If an atom has more electrons than the valence electrons around it in Lewis dot structure, then it will acquire a formal negative charge. If the electrons are less than the valence electrons, then it will acquire a formal positive charge.
Example:
Oxygen (O)
It has 6 valence electrons so it is very happy with two bonds and two lone pairs in the Lewis dot structures
Valence electrons of O = 6
No of bonds = 2
Lone pairs = 2
FC = 6-2-(2*2) =0
However if Oxygen has one bond with three lone pairs in Lewis dot structure, then
Valence electrons of O = 6
No of bonds = 1
Lone pairs = 3
FC = 6-2-(2*3) =-1
Another example:
Nitrogen (N)
It has 5 valence electrons so it is very happy with three bonds and one lone pair in the Lewis dot structures
Valence electrons of N = 5
No of bonds = 3
Lone pairs = 1
FC = 5-3-(2*1) =0
However if there are 4 bonds around N which we generally see in many ammonium compounds than it will acquire a formal positive charge
Valence electrons of N = 5
No of bonds = 4
Lone pairs = 0
FC = 5-4-(2*0) =+1
Yet another example:
Carbon (C)
It has 4 valence electrons so it is very happy with four bonds and no lone pairs in the Lewis dot structures.
Valence electrons of C = 4
No of bonds = 4
Lone pairs = 0
FC = 4-4-(2*0) =0
The atoms discussed above are in the second period of the periodic table and hence cannot have more than 8 electrons in the outermost shell (no expanded octet due to lack of d orbitals).
Expanded octet
Now, let’s take an element which can have an expanded octet.
Example:
Sulfur/Sulphur (S)
It has 6 valence electrons. So, like oxygen it is also very happy with zero formal charge on it. However, unlike oxygen it has more different combinations to get a zero formal charge. One of the combinations is just like oxygen atom (two bonds and two lone pairs)
Valence electrons of S = 6
No of bonds = 2
Lone pairs = 2
FC = 6-2-(2*2) =0
Second combination is four bonds and one lone pair .Here Sulfur has 10 electrons around it .(expanded octet and extra electrons are accommodated in the empty 3d orbitals of Sulfur).
Valence electrons of S = 6
No of bonds = 4
Lone pairs = 1
FC = 6-4-(2*1) = o
Third combination is 6 bonds and no lone pair . Here Sulfur has 12 electrons around it (expanded octet and extra electrons are accommodated in the empty 3d orbitals of sulfur)
Valence electrons of S = 6
Thiocyanate Ion Lewis Structure
No of bonds = 6
Lone pairs = 0
FC = 6-6-(2*0) =0
Phosphorus has 5 valence electrons so like nitrogen it is also very happy with zero formal charge on it. However, unlike nitrogen it has more different combinations to get zero formal charge .One feasible is just like nitrogen atom three bonds and one lone pair.
Valence electrons of P = 5
No of bonds = 3
Lone pairs = 1
FC = 5-3-(2*1) =0
Second feasible combination to get zero formal charge is five bonds around P . Here phosphorus is with 10 electrons around it (expanded octet and extra electrons are accommodated in the empty 3d orbitals of Phosphorous)
Valence electrons of P = 5
No of bonds = 5
Lone pairs = 0
FC = 5-5-2*0=0
Now let us apply step 3 on our molecule
SO2
From step 2 skeleton of the molecule is
Now let us complete the octet of the most electronegative element O first with minimum formal charge. As you have seen that oxygen is happy with two bonds and two lone pairs so very safely we can put a double bond and two lone pairs on each oxygen atom.
Let’s take nitrate ion as the next example.
In the nitrate ion – NO3−
From step 2 skeleton of the molecule is
Now let us complete the octet of the most electronegative atom O with minimum formal charge. Oxygen being terminal is very happy with a double bond and two lone pairs
Invalid structure : Central atom nitrogen can not have more than 8 electrons
This structure is wrong because N cannot have more than 8 electrons around it .In the above structure we have made 6 bonds around Nitrogen means 6*2 (2 electrons in each bond) =12 electrons .Now we need to replace two of the double bonds of the oxygen atom with nitrogen into single bond .To complete the octet of these oxygen, we need to put one extra lone pair on each of them and in the structure you can see two singly bonded oxygen atoms with three lone pairs.
STEP 4 : COMPLETE THE STRUCTURE
COMPLETE THE STRUCTURE BY PLACING THE REMAINING VALENCE ELECTRONS FROM THE TOTAL VALENCE ELECTRONS AS LONE PAIRS ON THE CENTRAL ATOM
Let’s understand this using an example:
In SO2 molecule
Total valence electrons = 18 (from step 1)
Last step is to calculate the total bond pairs and lone pairs placed in the molecule and subtract it from total valence electrons calculated in step 1
Lone pairs and bond pairs in Sulfur dioxide molecule
Number of electron used up to step 3 are

4 bond pairs and 4 lone pairs hence total is 4*2(Bond pair) +4*2 (lone pair) =16
No of electrons left unused = Total valence electrons – electrons used in Lewis dot structure
= 18-16 =2
These left electrons pair is put on the S atom
Now let us calculate the formal charge on each atom in the lewis dot structure of SO2 molecule
SO2 formal charge calculations
Now let us check for NO3– (nitrate ion)
Total valence electrons = 24
Electrons used are as 4 bond pairs and 8 lone pairs =4*2+8*2=24
Hence all 24 valence electrons are used up .
Let us calculate formal charge on each atom using the equation
FC = Valence electrons – No of bonds – 2*Lone pairs
Final Lewis dot structure of NO3– (nitrate ion)
Nitrate ion lewis dot structure
In brief we need to master 4 steps for making a correct Lewis dot structure
- Count total valence electrons in the molecule or ion.
- Select the central atom and make a skeleton of the molecule or ion.
- Complete the octet of the most electronegative atom with minimum formal charges.
Formal charge = Valence electrons – no of bonds – 2*Lone pairs
Or Formal charge = Group No – Bond pairs – 2*Lone pairs
- Complete the structure by placing unused electrons from the total valence electrons as lone pairs on the central atom.
Step 1
Total valence electrons = 5(N) + 4*1 (4 H s)-1 (due to one positive charge) = 8
Step 2
Phosphate Ion Lewis Structure
Central atom is N because H can never be the central atom and N is more EN than H. (remember mentioned earlier also)
Skeleton of NH4+
Step 3 is already taken care of ,as N has 8 electrons around it and each H is with two electrons on it .
Step 4 :
Total electrons used are as 4 bond pairs = 4*2 = 8
Formal charge on N= Valence electrons – no of bonds – 2*Lone pairs
5-4-0 = +1
Formal charge on H = Valence electrons – no of bonds – 2*Lone pairs
H+ Cation Lewis Structure
= 1-1-0 = 0
Final correct Lewis dot structure of ammonium ion is:
Step 1
Total valence electrons = 7(Cl) + 4*6 (4 SO)+1 (due to one negative charge) = 32
Step 2
Central atom is Cl because O is more electronegative than Cl (check the periodic table)
Skeleton of ClO4– ion
Step 3
Complete the octet of oxygen with minimum formal charge .
Oxygen being terminal is very happy with a double bond and two lone pairs
Invalid Lewis dot structure of perchlorate ion
Remember Cl can have maximum 7 bonds around it because it has 7 valence electrons. In the above structure Cl has 8 bonds around it which will give a negative formal charge to Cl. So this can be taken care if we replace one double bond of oxygen with a single bond and complete the octet of O with one lone pair.
(FC = Valence electrons – no of bonds – 2*Lone pairs)
Step 4:
Electrons used are as 7 bond pairs and 9 lone pairs = 7*2+9*2=32 electrons
Hence all valence electrons are used and no more electrons are left.
Final completed correct lewis dot structure of perchlorate ion is
Lewis dot structure of perchlorate ion